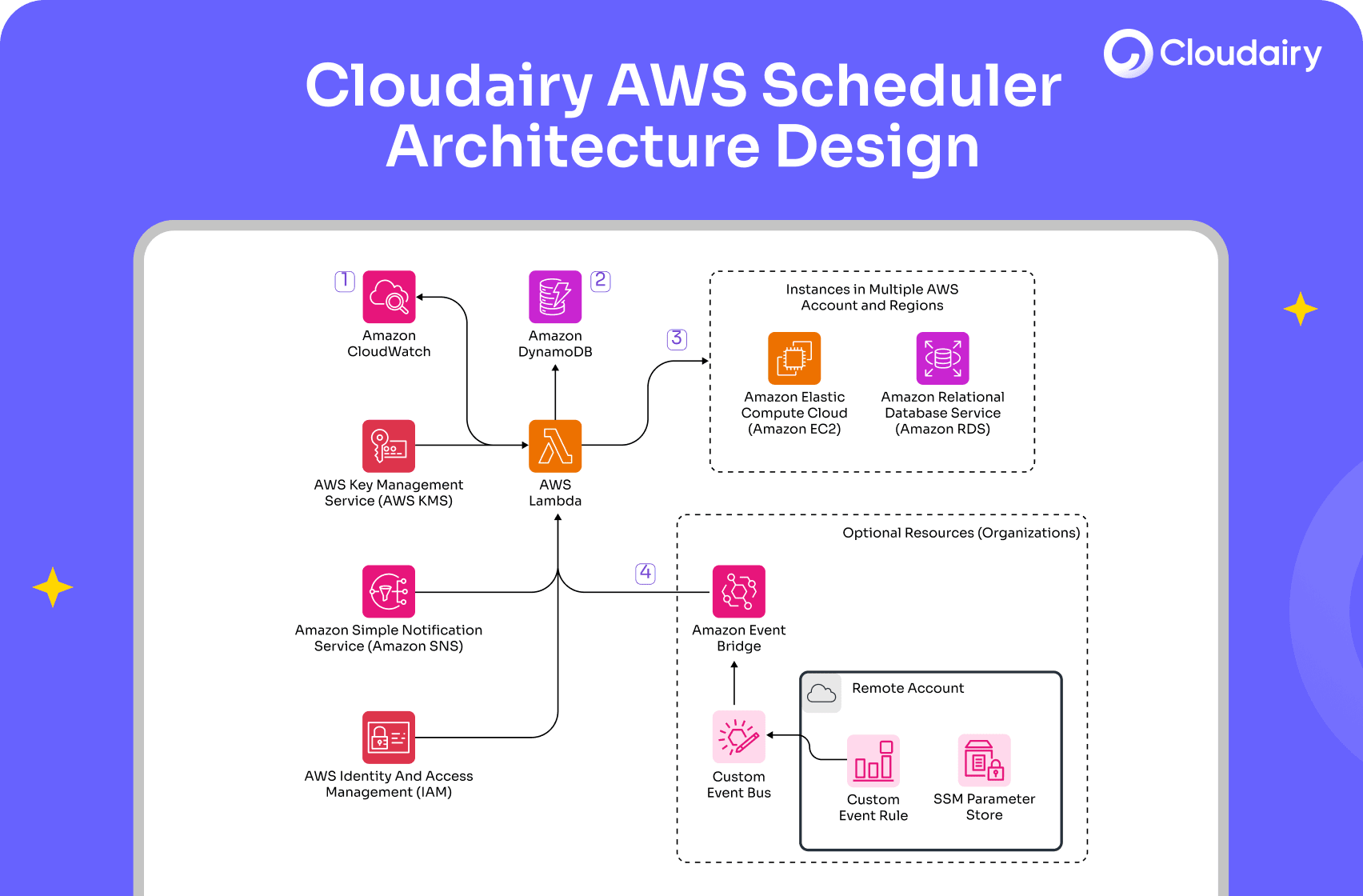
AWS Instance Scheduler Architecture Designed with Cloudairy Cloudchart

Get your team started in minutes
Sign up with your work email for seamless collaboration.

Managing cloud costs efficiently is crucial for businesses leveraging AWS resources. One effective way to optimize costs is by automating the start and stop times of your EC2 instances using AWS Instance Scheduler. This comprehensive blog will walk you through the process of setting up an AWS Instance Scheduler to help you manage your resources efficiently.
Step 1: Prerequisites
Before beginning the setup of the AWS Instance Scheduler, ensure you have the following
Step 2: Launch AWS Instance Scheduler
AWS provides a CloudFormation template to simplify the deployment of the Instance Scheduler. Follow these steps:
Access the CloudFormation Console
Specify Stack Details
Optionally, configure stack options like tags, permissions, and advanced settings. and click "Next."
Review and Create
Create Stack: Click "Create stack."
Step 3: Create a Schedule
Once the CloudFormation stack is created, you need to define the schedules that control when instances are started and stopped.
Navigate to DynamoDB
Access the Schedule Table
Add a New Schedule
Click on "Items" and then "Create item"
Add a new item with the following attributes.
Save the Schedule
Once you have entered the details, save the item.
Step 4: Tag Instances
To apply the schedule to your EC2 instances, you need to tag them appropriately.
Navigate to EC2 Console
Select Instances
Add Tags
Save Changes
Step 5: Verify and Monitor
Check CloudWatch Logs
Monitor Instances
Security and Permissions
When setting up AWS Instance Scheduler, it's crucial to consider the security implications and configure permissions accordingly:
1. IAM Permissions: Ensure that the IAM role used by the Instance Scheduler has the necessary permissions to start and stop EC2 instances.
2. DynamoDB Table Permissions:
Optimizing Schedules
To maximize cost savings, consider the following best practices when defining schedules:
3. Non-Production Environments:
4. Multi-Region Support:
5. Custom Schedules:
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
1. CloudWatch Metrics:
2. Debugging Logs:
Updating and Maintaining the Solution
To keep your AWS Instance Scheduler up to date:
Alternative Cost Optimization Strategies
While the AWS Instance Scheduler is a powerful tool, consider combining it with other strategies for comprehensive cost management:
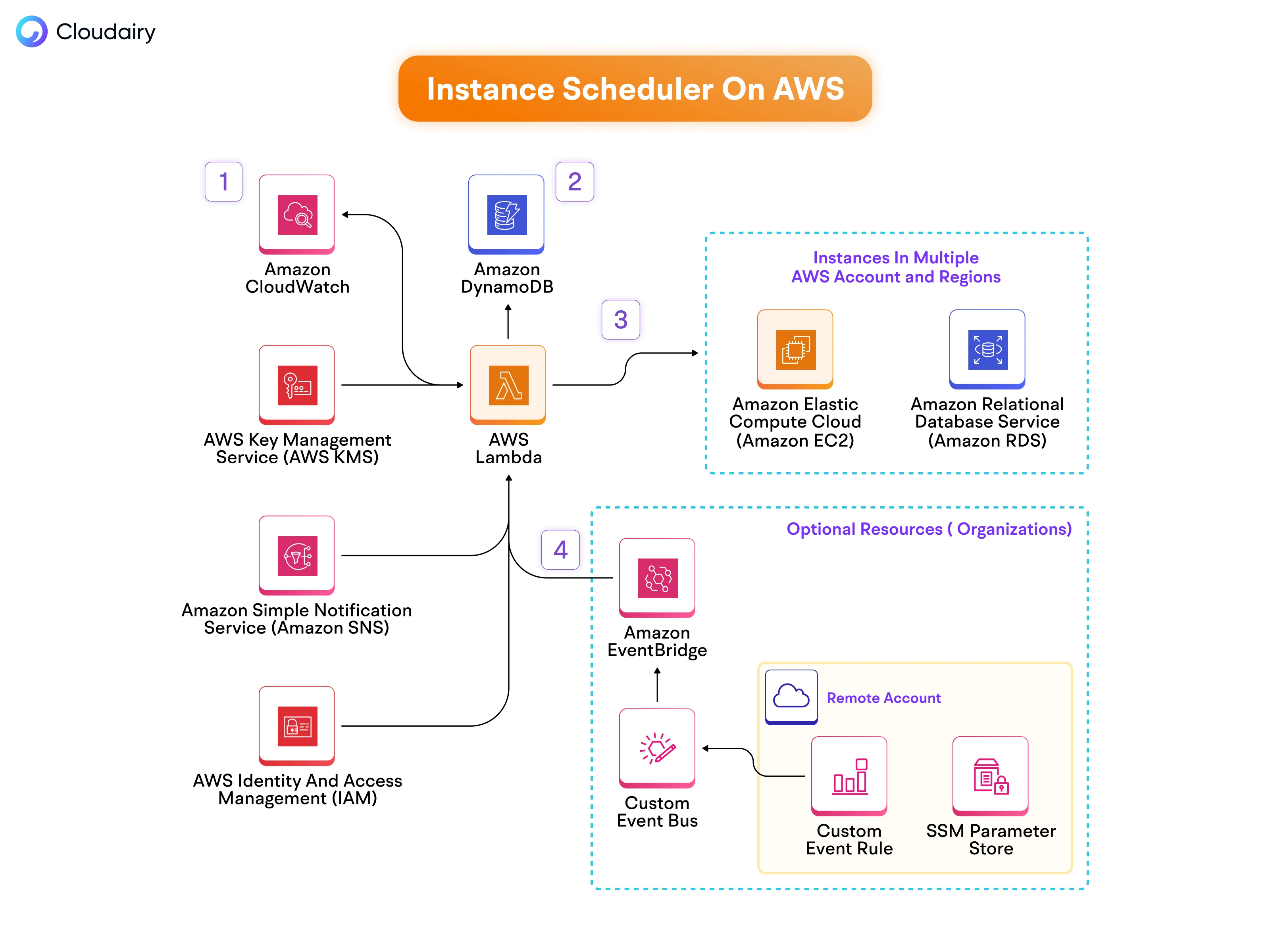
Setting up an AWS Instance Scheduler is an excellent step towards automating your EC2 instance management and reducing cloud costs. The above blog has walked you through launching the scheduler, creating schedules, tagging instances, and monitoring the solution. By following these steps, your organization can implement a seamless and automated solution to manage EC2 instance usage effectively. Moreover, combining this with other AWS cost optimization strategies can lead to substantial savings and improved resource management.
Start using Cloudairy to design diagrams, documents, and workflows instantly. Harness AI to brainstorm, plan, and build—all in one platform.